top of page
ALEX DEAN
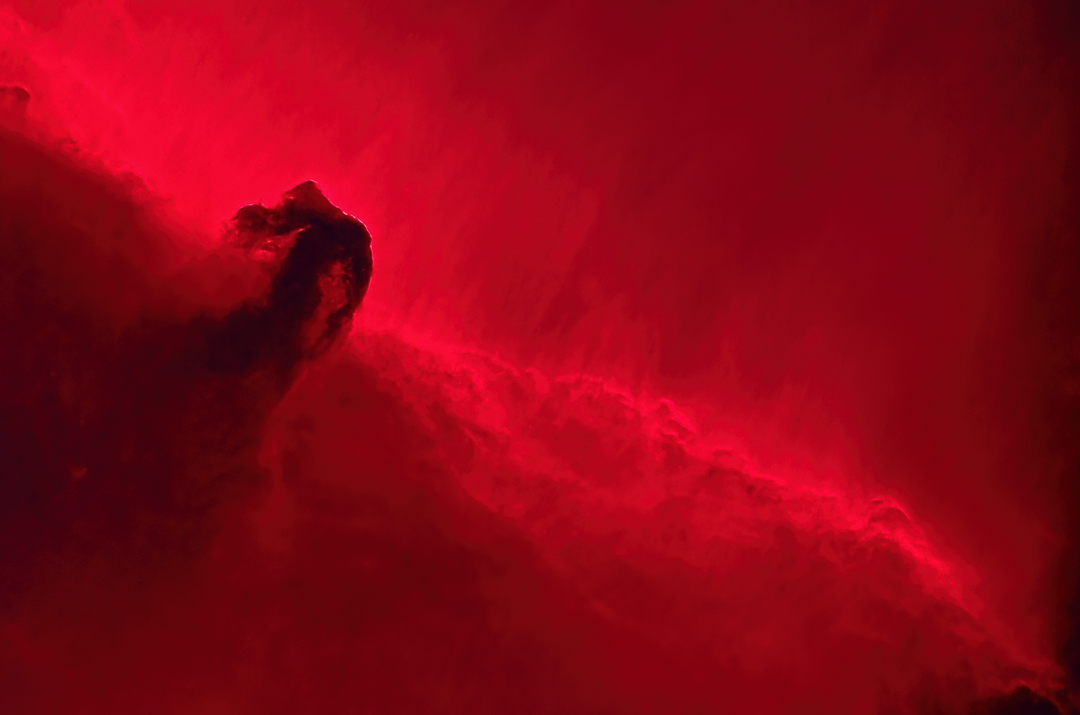
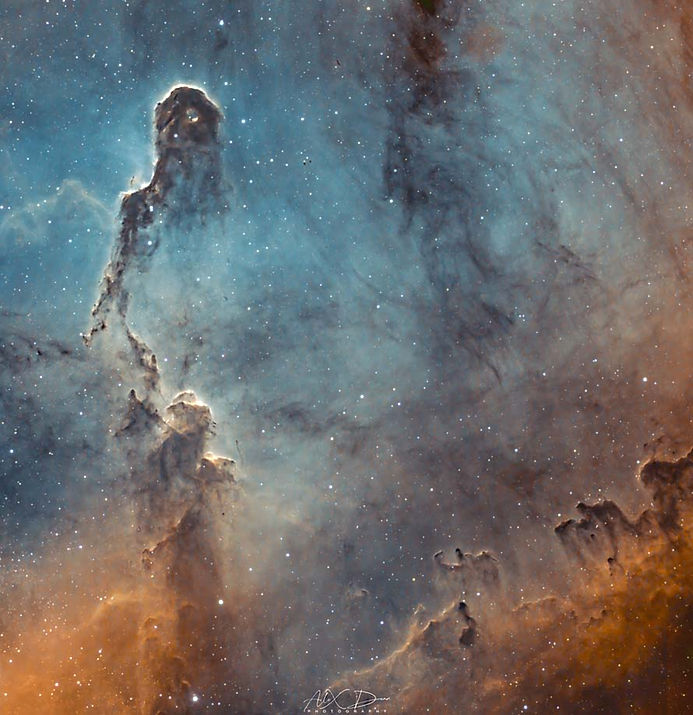




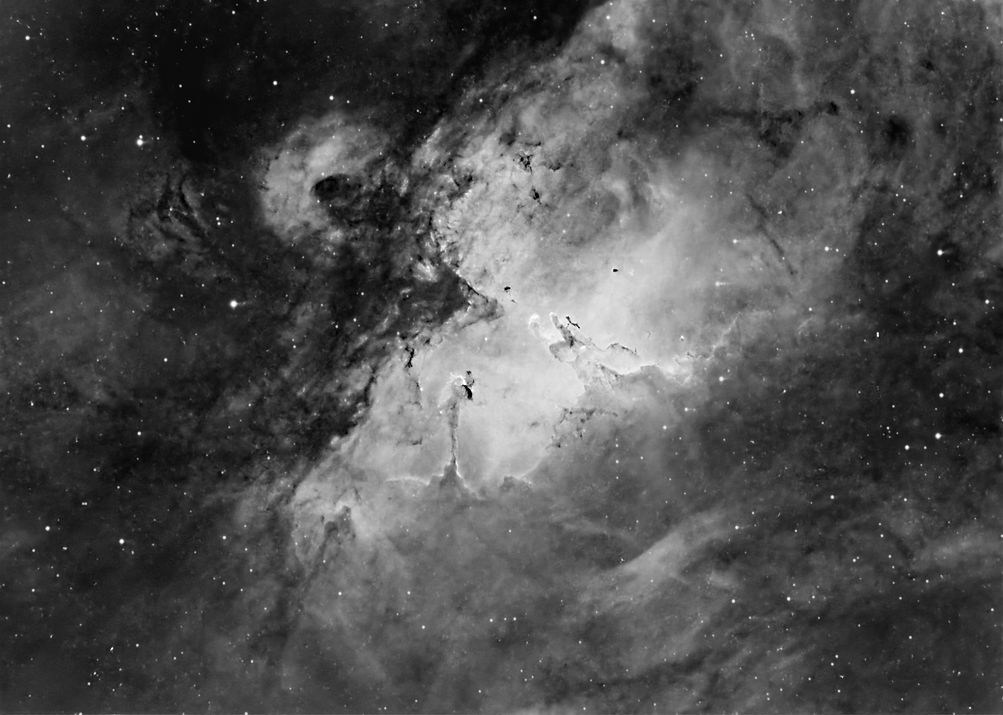
The Elephant's Trunk Nebula is a concentration of interstellar gas and dust within the much larger ionized gas region IC 1396 located in the constellation Cepheus about 2,400 light years away from Earth.[1] The piece of the nebula shown here is the dark, dense globule IC 1396A; it is commonly called the Elephant's Trunk nebula because of its appearance at visible light wavelengths, where there is a dark patch with a bright, sinuous rim. The bright rim is the surface of the dense cloud that is being illuminated and ionized by a very bright, massive star (HD 206267) that is just to the east of IC 1396A. (In the Spitzer Space Telescope view shown, the massive star is just to the left of the edge of the image.) The entire IC 1396 region is ionized by the massive star, except for dense globules that can protect themselves from the star's harsh ultraviolet rays.
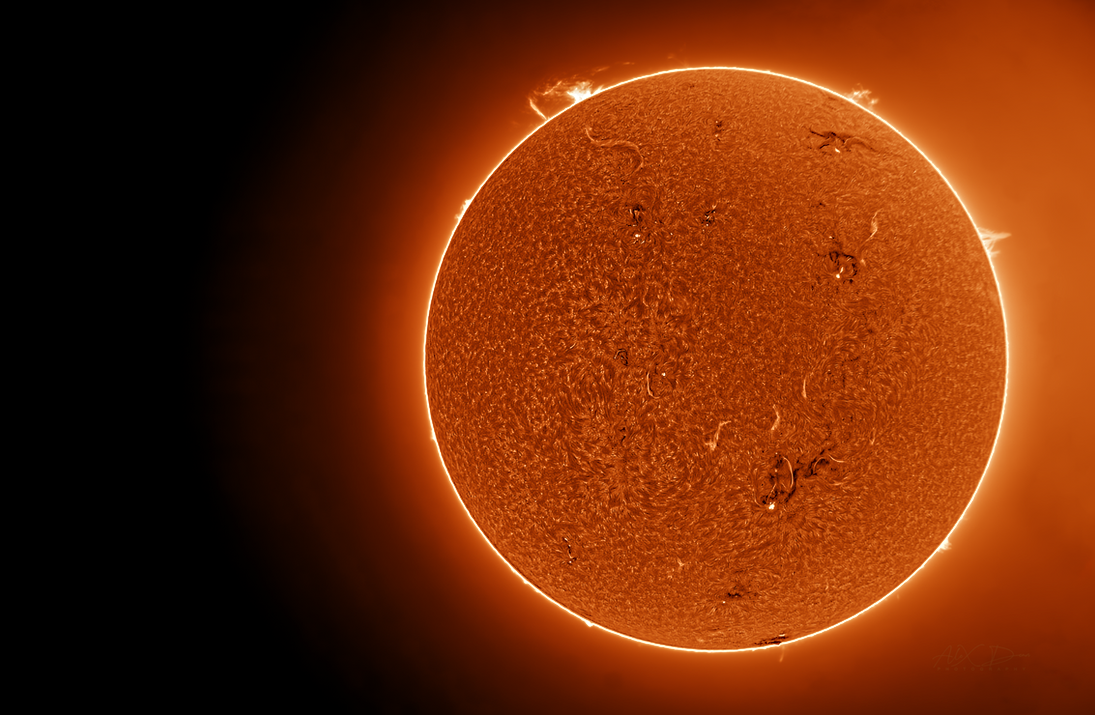
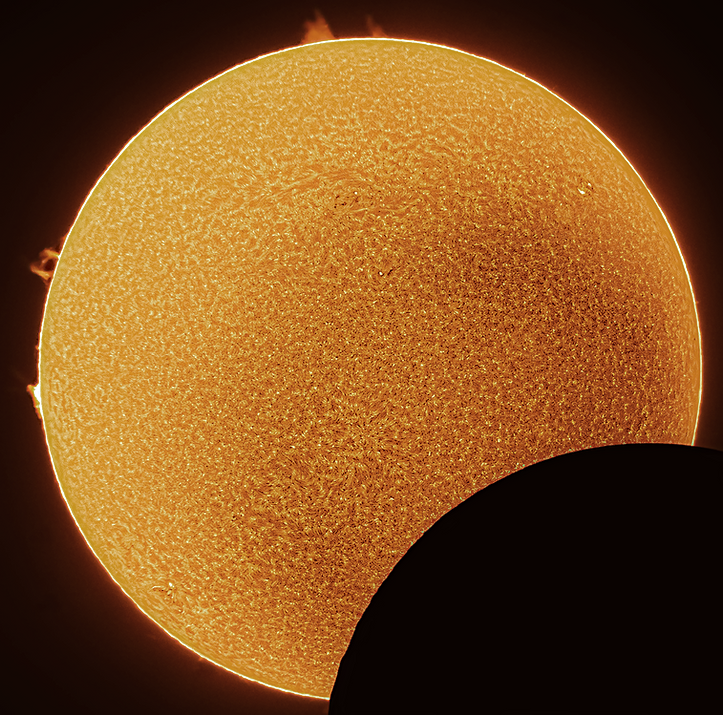





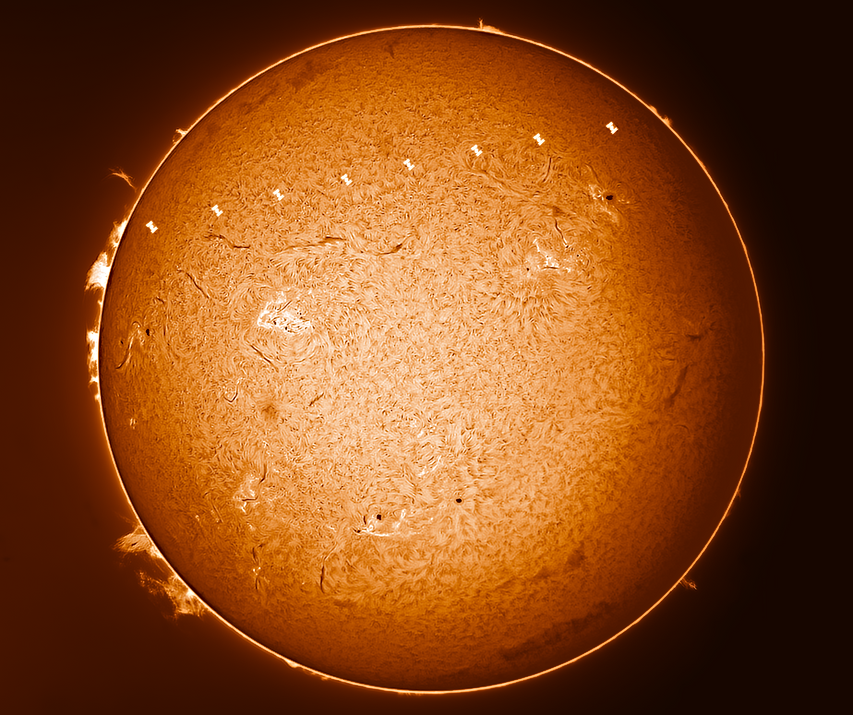


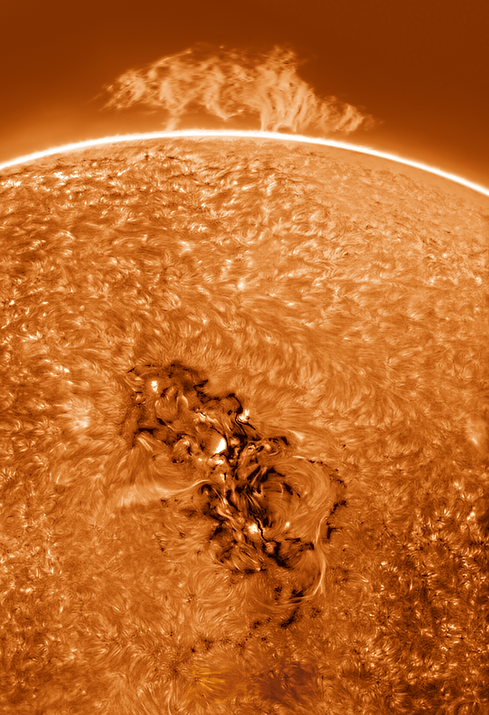
Full Solar Disk.
Astonomy Magazine Photo of the day 28th October 2022
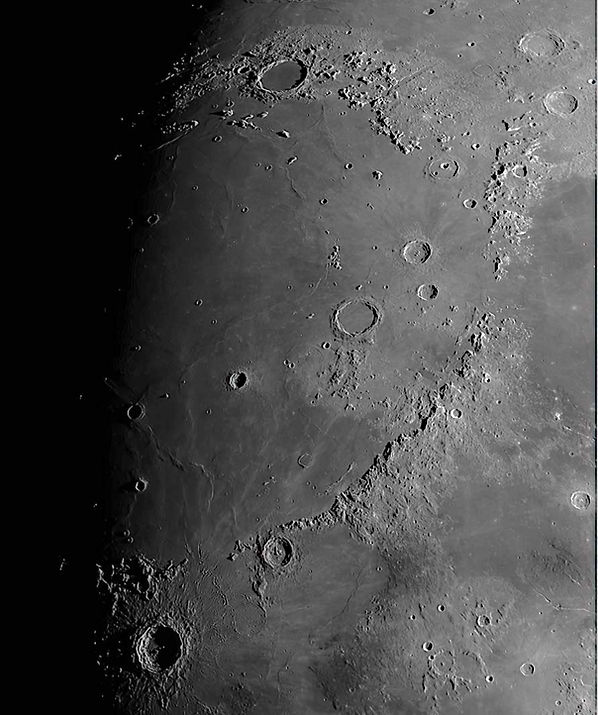

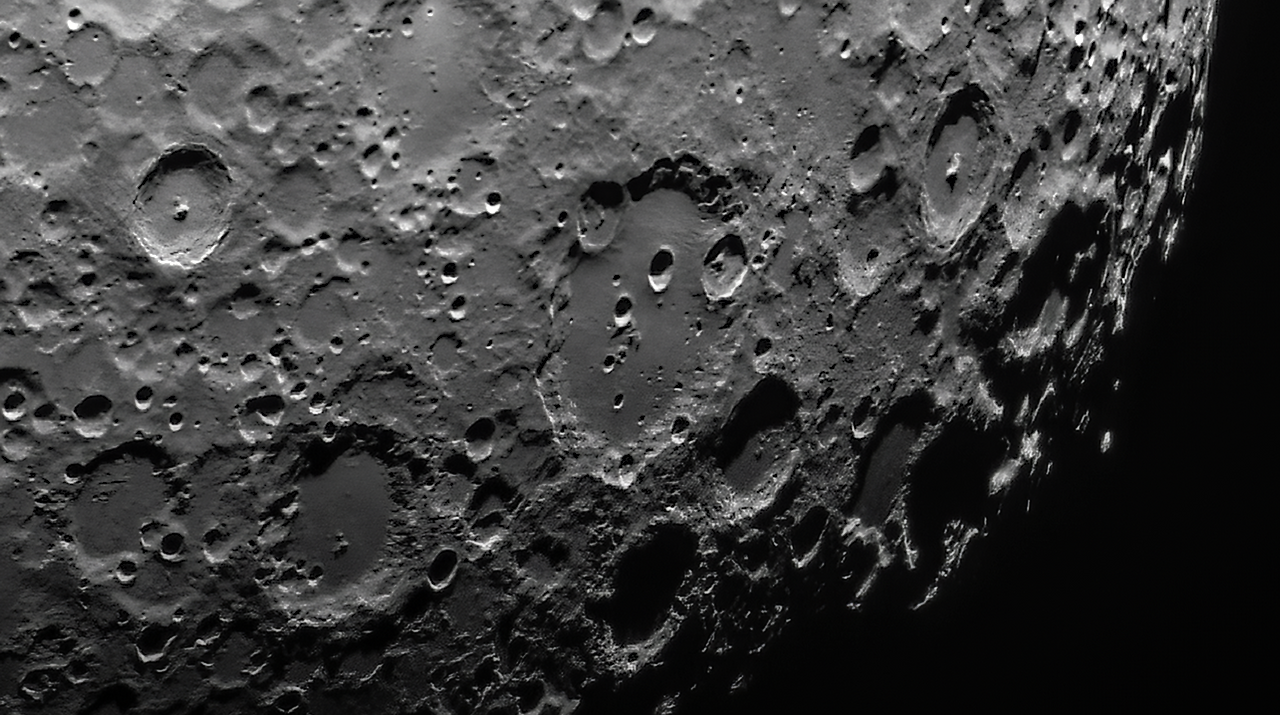
The Moon. Apollo 14 landing site bottom left. Rupus Recta wall top/middle
The landing site is located in a broad, shallow valley between radial ridges of the Fra Mauro Formation and approximately 500 kilometers from the edge of the Imbrium Basin. The major crater Copernicus lies 360 kilometers to the north, and bright ray material that emanates from Copernicus Crater covers much of the landing site region. In the immediate landing site area, an important feature is the young, very blocky Cone Crater, which is approximately 340 meters in diameter and which penetrates the regolith on the ridge to the east of the landing site.
Rupes Recta is a linear fault on the Moon, in the southeastern part of the Mare Nubium at 22.1°S 7.8°W. The name is Latin for straight cliff, although it is more commonly called the Straight Wall. This is the most well-known escarpment on the Moon
Rupes Recta is a linear fault on the Moon, in the southeastern part of the Mare Nubium at 22.1°S 7.8°W. The name is Latin for straight cliff, although it is more commonly called the Straight Wall. This is the most well-known escarpment on the Moon
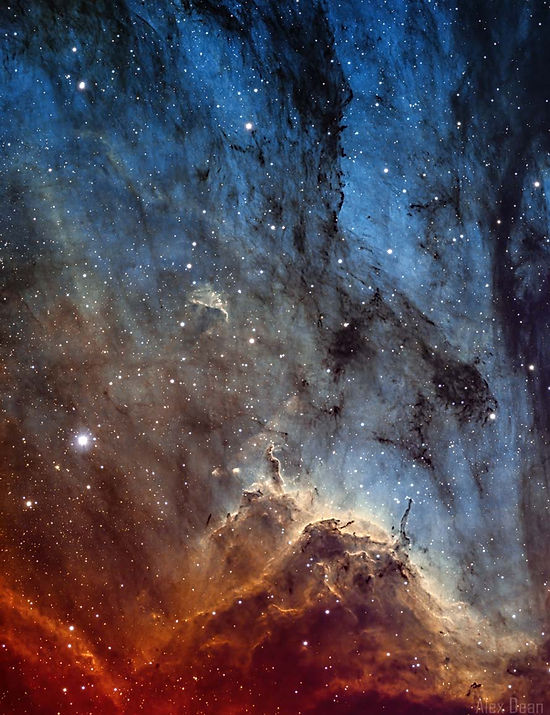
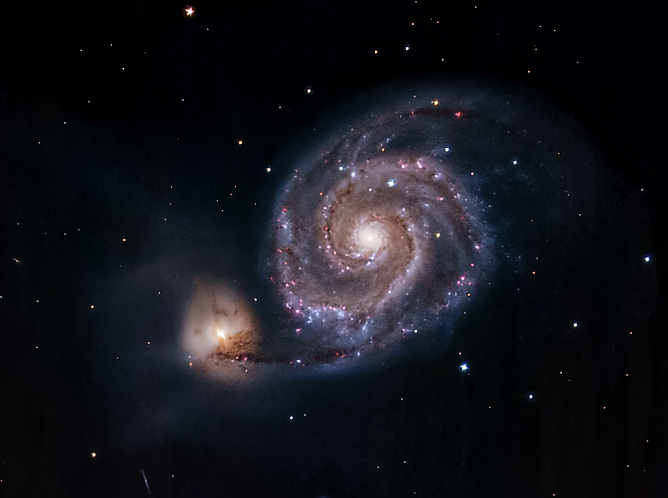
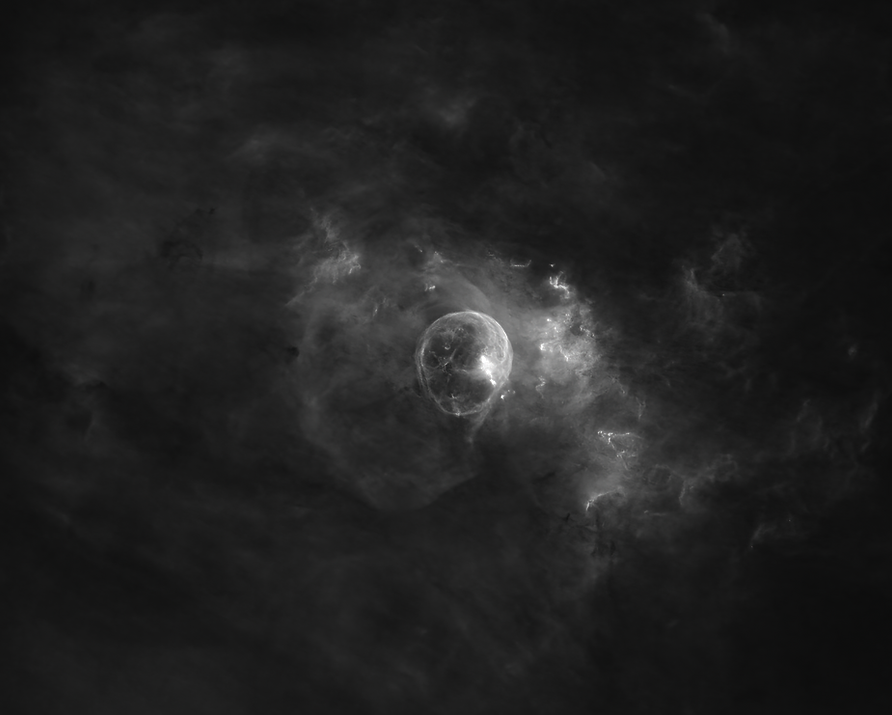
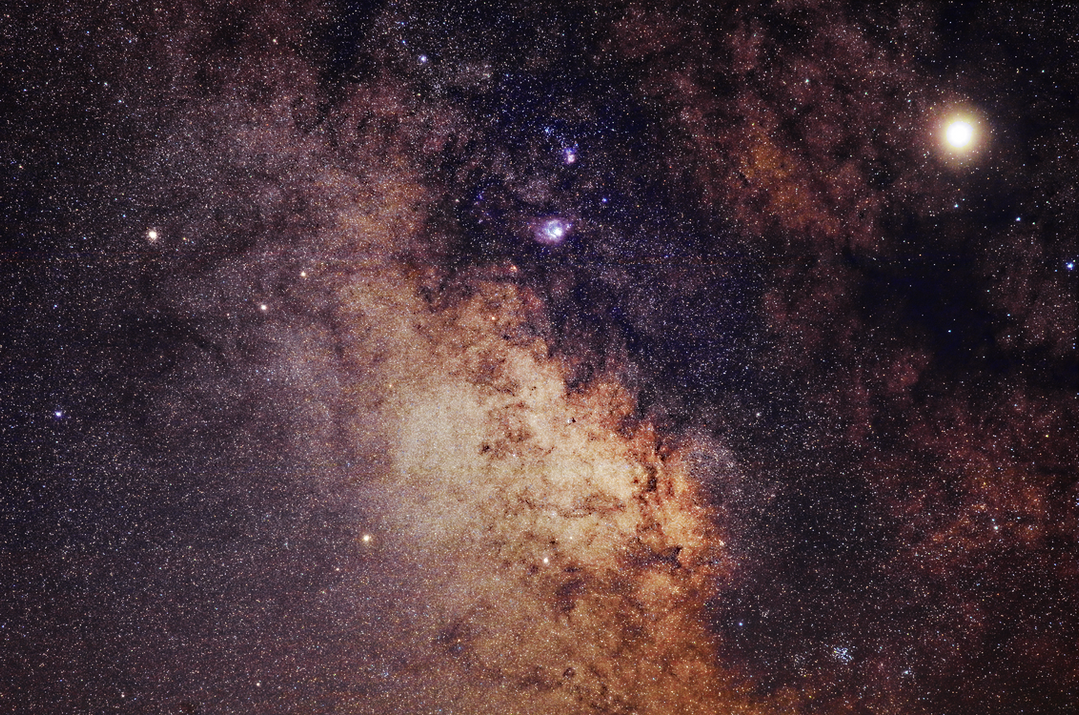








Comet A6 Lemmon 2025




The Elephant's Trunk Nebula is a concentration of interstellar gas and dust within the much larger ionized gas region IC 1396 located in the constellation Cepheus about 2,400 light years away from Earth.[1] The piece of the nebula shown here is the dark, dense globule IC 1396A; it is commonly called the Elephant's Trunk nebula because of its appearance at visible light wavelengths, where there is a dark patch with a bright, sinuous rim. The bright rim is the surface of the dense cloud that is being illuminated and ionized by a very bright, massive star (HD 206267) that is just to the east of IC 1396A. (In the Spitzer Space Telescope view shown, the massive star is just to the left of the edge of the image.) The entire IC 1396 region is ionized by the massive star, except for dense globules that can protect themselves from the star's harsh ultraviolet rays.








Full Solar Disk.
Astonomy Magazine Photo of the day 28th October 2022

The Moon. Apollo 14 landing site bottom left. Rupus Recta wall top/middle
The landing site is located in a broad, shallow valley between radial ridges of the Fra Mauro Formation and approximately 500 kilometers from the edge of the Imbrium Basin. The major crater Copernicus lies 360 kilometers to the north, and bright ray material that emanates from Copernicus Crater covers much of the landing site region. In the immediate landing site area, an important feature is the young, very blocky Cone Crater, which is approximately 340 meters in diameter and which penetrates the regolith on the ridge to the east of the landing site.
Rupes Recta is a linear fault on the Moon, in the southeastern part of the Mare Nubium at 22.1°S 7.8°W. The name is Latin for straight cliff, although it is more commonly called the Straight Wall. This is the most well-known escarpment on the Moon
Rupes Recta is a linear fault on the Moon, in the southeastern part of the Mare Nubium at 22.1°S 7.8°W. The name is Latin for straight cliff, although it is more commonly called the Straight Wall. This is the most well-known escarpment on the Moon








Comet A6 Lemmon 2025
bottom of page